Gaea is built around a very powerful, flexible, and extensible core. With Gaea 2.1.1 we introduced a range of new advanced power-user features that can help you transform a Gaea project into a parametric powerhouse.
The three core features introduced are Variables, Expressions, and Exposed Properties, with the powerful Math Node as a bonus for fully custom logic.
Variables, Expressions, and Exposed Properties
Variables.
Define a variable such as Float, Integer, Choice, Bool, Color, or String. These variables can be bound to different properties on across the graph. Variables can be controlled through the UI or the command line.
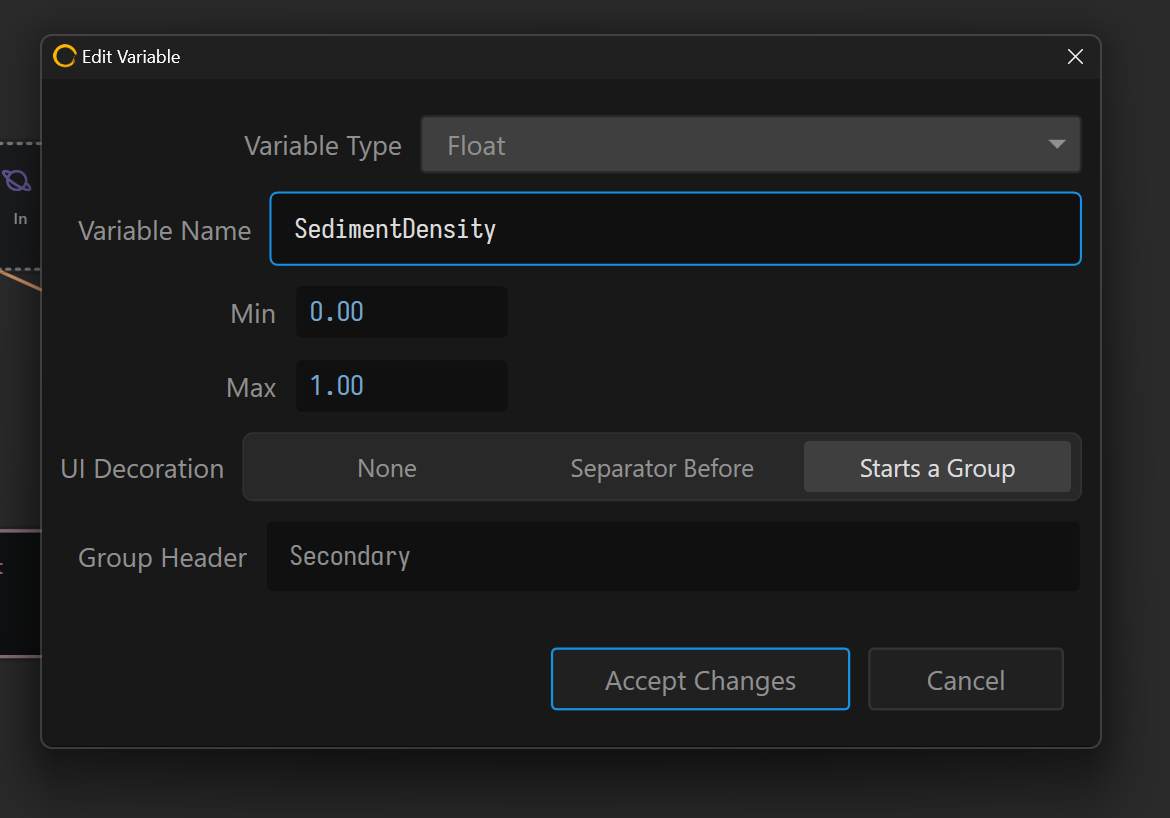
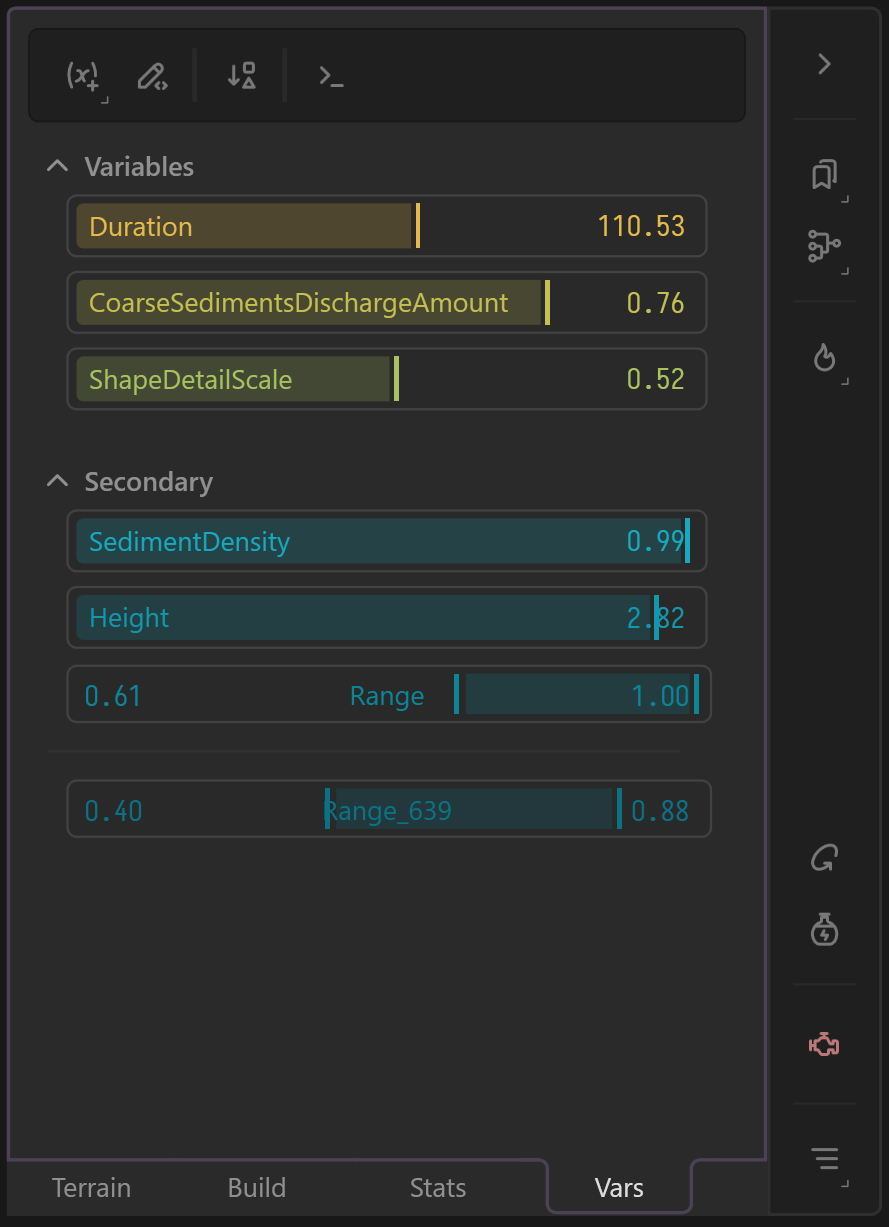
Expressions.
Expressions are modifiers applied to either a property, such as a slider, or to the variable bound to the property. It allows you to make modifications to the incoming value.
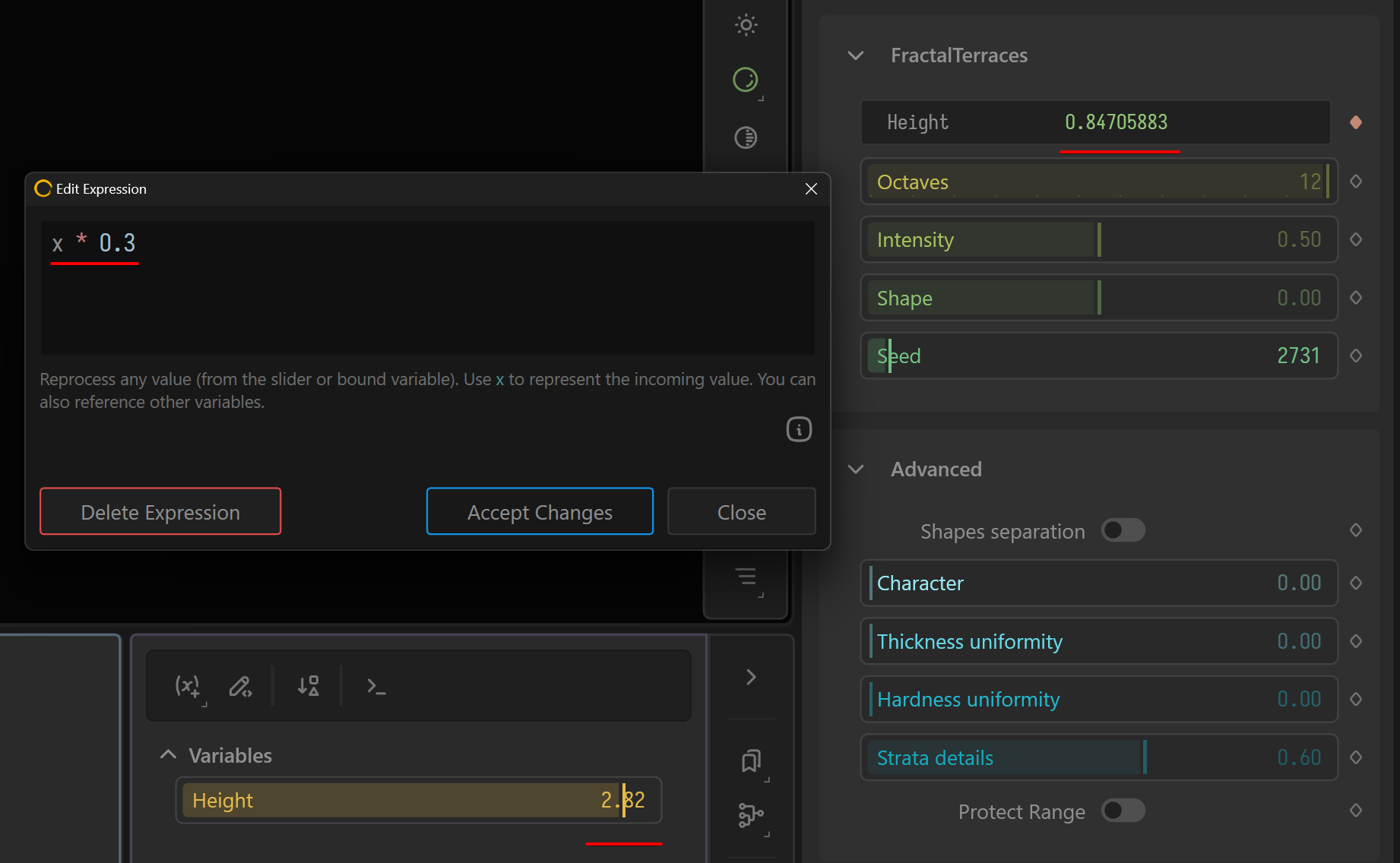
Exposed Properties.
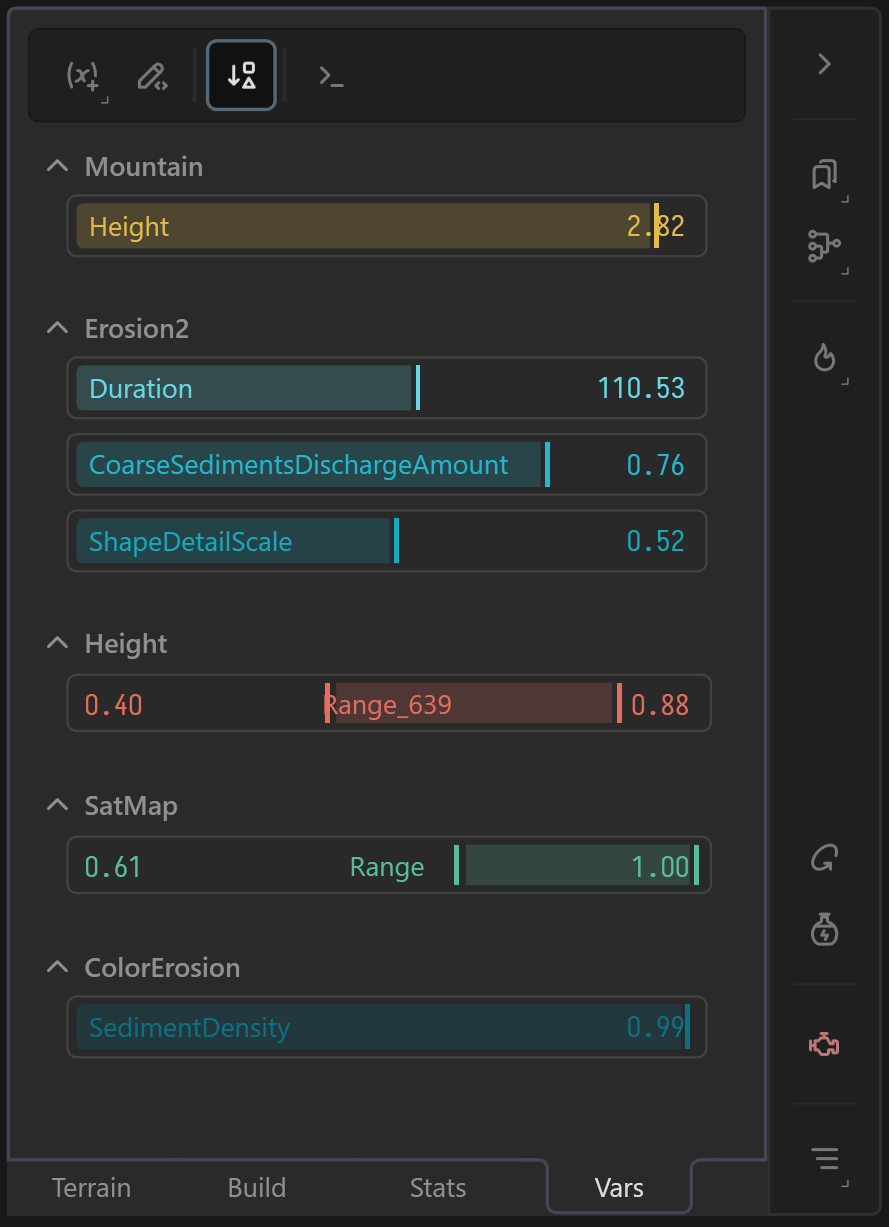
This not a direct feature but a byproduct of Variables. You can expose a specific property from a node, and have it be available just like other Variables and edit your node from the Variable Editor panel.
See the Feature Preview video on our YouTube Channel.
🧭 For more detailed information, see the Variables documentation.
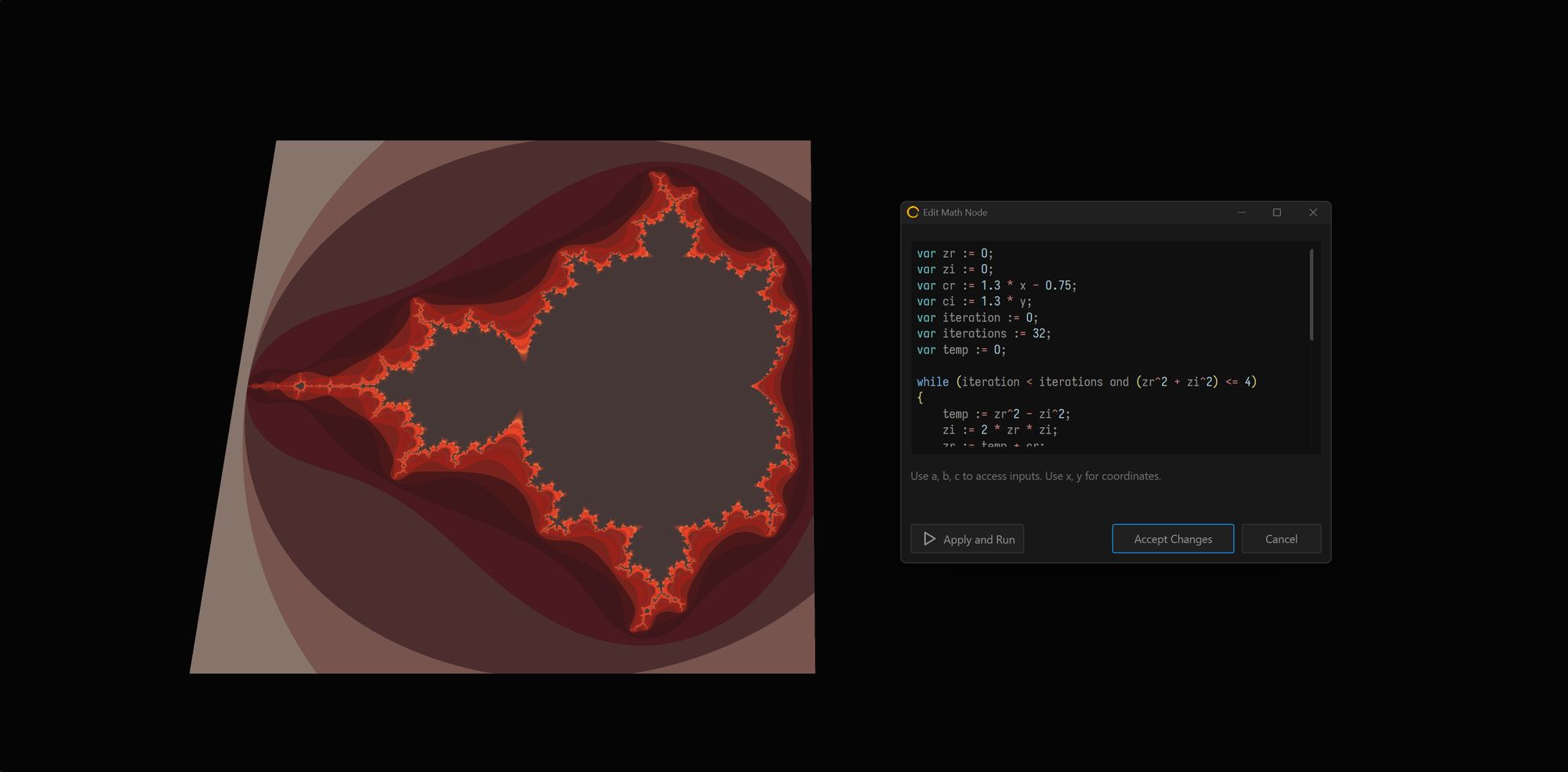
Math Node.
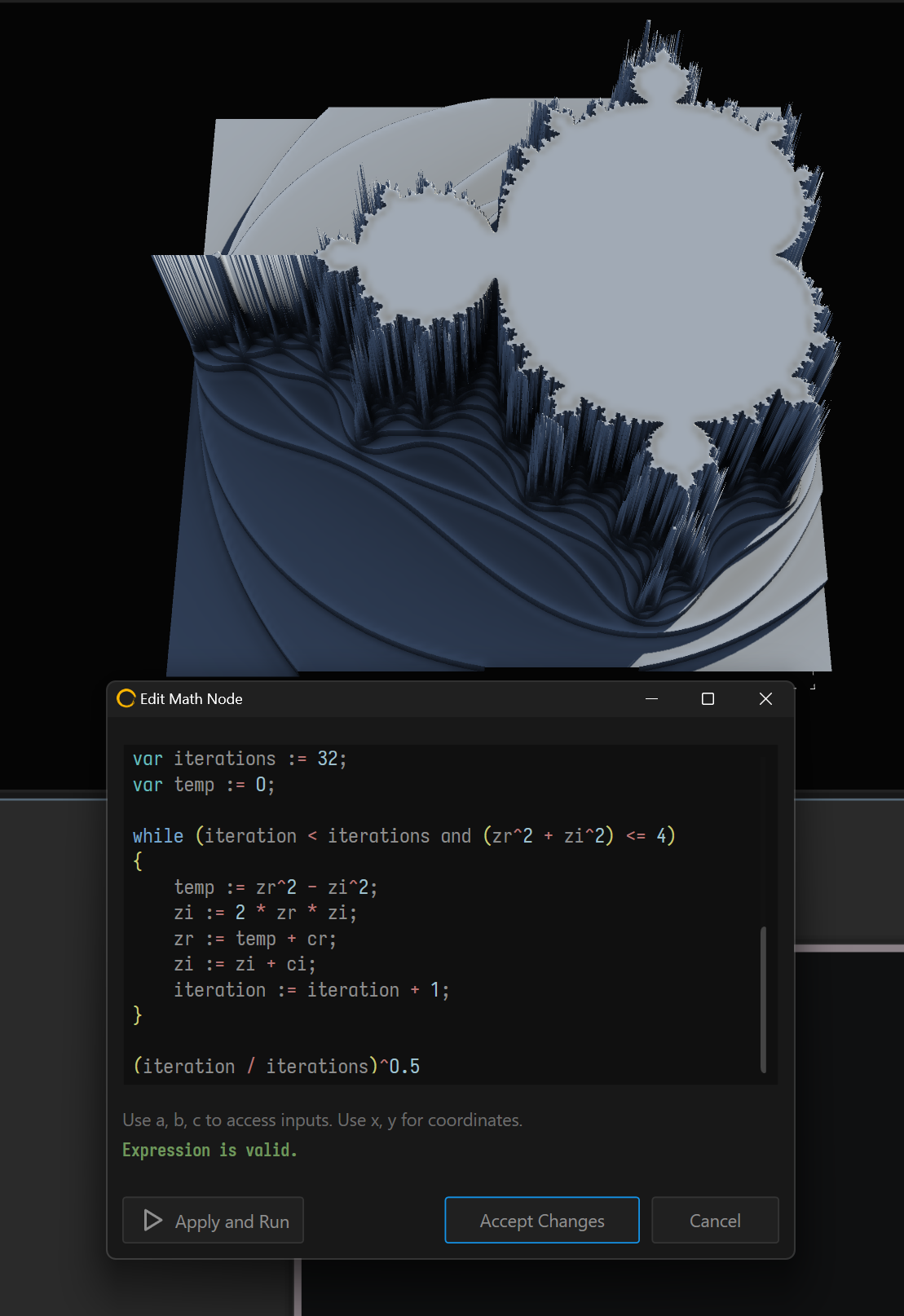
The Math node can work standalone as a Generator, but can also accept up to 3 inputs. These inputs can be accessed as a,b,c respectively. Note, those are pre-defined variables and can't be used for any other purposes except to access data from the port.
You can also access coordinates per-pixel using x and y .
Syntax and Functions
The Math node can accept the following.
// Mathematical operators
+, -, *, /, %, ^
// Equalities & Inequalities
=, ==, <>, !=, <, <=, >, >=
// Assignment
:=, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=
// Logical operators
and, nand, nor, not, or, xor, xnor, mand, mor
// Functions
abs, avg, ceil, clamp, erf, erfc, exp, expm1, floor, frac,
hypot, iclamp, inrange, log, log10, log1p, log2, logn, max,
min, mod, mul, ncdf, pow, root, round, roundn, sgn, sqrt,
sum, swap, trunc, equal, not_equal
// Trigonometry
acos, acosh, asin, asinh, atan, atan2, atanh, cos, cosh,
cot, csc, sec, sin, sinc, sinh, tan, tanh, deg2rad,
rad2deg, deg2grad, grad2deg
// Control structures
if-then-else, ternary conditional, switch case, return-statement
// Loop structures
while loop, for loop, repeat until loop, break, continue
// Expression local variables, vectors and strings
// User defined variables, vectors, strings, constants and function support